What states don’t need car insurance? It’s a question that often arises, especially for those looking to save money on their monthly expenses. While some states mandate car insurance, others have opted for a different approach, relying on financial responsibility laws instead. This means that drivers in these states aren’t required to have insurance but are responsible for proving they can cover any damages or injuries they might cause in an accident.
This approach raises several questions. What are the potential risks and consequences of driving without insurance in these states? Are there alternative insurance options available? And what are the implications for drivers who choose to go without coverage? Exploring these questions is crucial for understanding the complexities of car insurance in states that don’t require it.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance

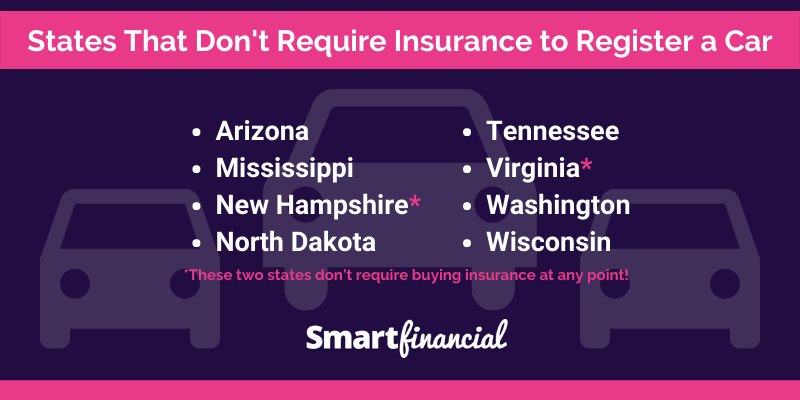
In the United States, all states mandate that drivers carry some form of liability insurance, except for two: New Hampshire and Virginia. These states have unique exceptions and provisions that allow drivers to choose whether or not to purchase insurance, but there are consequences for choosing not to do so.
Rationale for No Mandatory Car Insurance
These states have chosen not to mandate car insurance for a variety of reasons, including:
- Financial Freedom: Some argue that individuals should have the freedom to choose whether or not to purchase insurance and bear the financial risk themselves. They believe that mandatory insurance restricts individual choice and increases costs.
- Lower Costs: Proponents of no-fault insurance systems argue that they can lead to lower insurance premiums, as drivers are not required to pay for the costs of others’ injuries.
- Personal Responsibility: These states may believe that individuals should be responsible for their own actions and the consequences of their driving decisions. They argue that mandatory insurance can create a sense of complacency and encourage risky behavior.
Potential Risks and Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
While these states do not require car insurance, it is important to understand the potential risks and consequences of driving without it:
- Financial Ruin: In the event of an accident, a driver without insurance could be held liable for all damages, including medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages. This could lead to significant financial hardship, including the loss of assets and even bankruptcy.
- License Suspension: Even though car insurance is not mandatory, drivers in these states may still face license suspension if they are involved in an accident without insurance. This could make it difficult or impossible to drive legally and could lead to other consequences, such as job loss or difficulty obtaining a loan.
- Legal Action: In the event of an accident, the other driver could sue for damages, and a driver without insurance would have no financial protection. This could lead to a significant judgment against them, which they would be responsible for paying.
- Higher Costs: Drivers who choose not to purchase insurance may face higher costs in the long run, as they will be responsible for paying for any repairs or medical expenses themselves. Additionally, they may find it difficult to obtain a loan or rent a car without insurance.
Financial Responsibility Laws
Financial responsibility laws are designed to ensure that drivers have the means to cover the costs of any accidents they may cause. These laws typically require drivers to prove they have sufficient financial resources, usually through car insurance.
Financial Responsibility Laws in States with Mandatory Car Insurance
In states with mandatory car insurance, financial responsibility laws are generally enforced through the requirement to purchase car insurance. Drivers are required to carry proof of insurance, such as an insurance card, and provide this to law enforcement upon request. Failure to maintain car insurance can result in fines, license suspension, and even vehicle impoundment.
Financial Responsibility Laws in States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
States without mandatory car insurance rely on other mechanisms to ensure financial responsibility. These may include:
- Financial Responsibility Bonds: Drivers may be required to post a bond with the state, guaranteeing their ability to pay for damages in the event of an accident. This bond acts as a financial safety net for potential victims.
- Proof of Financial Responsibility: Some states require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, such as a deposit of a specific amount of money with the state or a letter from a bank confirming a sufficient amount of funds.
- Self-Insurance: Some states allow drivers to self-insure, meaning they are financially responsible for any damages they cause. This option requires drivers to demonstrate a high level of financial stability and responsibility.
Potential Legal and Financial Implications of Violating Financial Responsibility Laws
Violating financial responsibility laws can have serious consequences, including:
- Fines and Penalties: Drivers who fail to meet financial responsibility requirements may face significant fines and penalties, which can vary by state.
- License Suspension: Driving without insurance or other proof of financial responsibility can lead to license suspension, preventing drivers from operating a vehicle legally.
- Vehicle Impoundment: In some cases, vehicles may be impounded until the driver meets financial responsibility requirements.
- Legal Liability: Drivers who are involved in an accident without proper insurance or financial responsibility may be held personally liable for all damages, including medical bills, property damage, and lost wages. This can result in substantial financial burdens and even bankruptcy.
Alternatives to Traditional Car Insurance
While some states don’t require car insurance, it’s still a good idea to have some form of financial protection in case of an accident. If you live in a state without mandatory car insurance, you can explore alternative options that offer coverage for your car and liability in case of an accident. These alternatives can be a good option for drivers who want more control over their insurance coverage and potentially lower premiums.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance is a strategy where you choose not to buy car insurance and instead set aside funds to cover potential costs related to accidents. This approach requires a high level of financial responsibility and careful planning.
Advantages of Self-Insurance
- Potential cost savings: If you have a good driving record and are willing to take on the financial risk, self-insurance could potentially save you money compared to traditional insurance premiums.
- Greater control over your coverage: You decide how much money to set aside and how to invest it, giving you more control over your coverage and financial planning.
Disadvantages of Self-Insurance
- High financial risk: You’re fully responsible for covering all costs related to an accident, including repairs, medical bills, and legal fees. This could lead to significant financial hardship if you’re involved in a major accident.
- Limited coverage: Self-insurance doesn’t cover all types of potential losses, such as damage to your car from natural disasters or theft.
- Potential legal issues: In some states, self-insurance might not be legally recognized, leaving you vulnerable to lawsuits and penalties.
Suitability of Self-Insurance
Self-insurance might be suitable for drivers with a strong financial foundation, a clean driving record, and a willingness to accept a high level of financial risk. It’s crucial to assess your financial situation and carefully consider the potential consequences before opting for self-insurance.
Surety Bonds, What states don’t need car insurance
A surety bond is a type of insurance that guarantees payment to a third party in case of a specific event, such as an accident. In the context of car insurance, a surety bond acts as a financial guarantee to cover your liability in case you’re responsible for an accident.
Advantages of Surety Bonds
- Potential cost savings: Surety bonds can be less expensive than traditional car insurance, especially for drivers with good driving records.
- Coverage for specific liabilities: Surety bonds provide coverage for specific types of liabilities, such as bodily injury and property damage, but may not cover other potential losses.
Disadvantages of Surety Bonds
- Limited coverage: Surety bonds typically offer limited coverage compared to traditional car insurance.
- Potential for financial hardship: If you’re involved in a major accident, the bond might not cover all costs, leaving you responsible for the remaining expenses.
- Complexity of the process: Obtaining a surety bond can be more complex than purchasing traditional car insurance.
Suitability of Surety Bonds
Surety bonds might be suitable for drivers who want a more affordable alternative to traditional car insurance and are comfortable with limited coverage. However, it’s important to carefully evaluate your needs and consider the potential financial risks before opting for a surety bond.
Risks of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without car insurance is a risky decision that can have severe consequences. It’s not just about avoiding a hefty fine; it’s about protecting yourself and others from the financial and legal burdens that can arise from an accident.
Financial Risks
Driving without insurance exposes you to significant financial risks. If you’re involved in an accident, you could be held liable for the costs of repairs, medical bills, lost wages, and other expenses related to the accident.
- Repair Costs: Even a minor fender bender can result in thousands of dollars in repair costs. If you’re at fault, you’ll be responsible for paying for the repairs to the other vehicle, and potentially your own.
- Medical Bills: Injuries sustained in an accident can lead to substantial medical expenses. If you’re uninsured, you’ll be responsible for these costs, which can quickly deplete your savings and leave you in debt.
- Lost Wages: If you’re injured in an accident and unable to work, you’ll lose income. Without insurance, you’ll have to cover these lost wages out of pocket.
- Legal Fees: If you’re sued by the other driver, you’ll need to hire an attorney to represent you in court. Legal fees can be expensive, and if you lose the case, you could be ordered to pay a significant judgment.
Legal Risks
Driving without insurance is a violation of the law in most states, and you could face serious legal consequences.
- Fines and Penalties: States impose fines and penalties on drivers who are caught driving without insurance. These fines can be substantial and can vary depending on the state and the number of offenses.
- License Suspension: If you’re caught driving without insurance multiple times, your driver’s license could be suspended. This means you’ll be unable to drive legally, making it difficult to get to work, school, or other essential destinations.
- Jail Time: In some states, driving without insurance can result in jail time, especially if you’re involved in an accident that causes serious injuries or death.
Personal Risks
Driving without insurance can have serious personal consequences. Beyond the financial and legal ramifications, it can also impact your reputation and your ability to obtain future insurance.
- Reputation Damage: If you’re involved in an accident and found to be uninsured, your reputation could be damaged. This could make it difficult to find employment or secure loans.
- Future Insurance Costs: Even if you eventually get insurance, your premiums will likely be higher than they would have been if you had maintained coverage. Insurance companies consider driving history and past claims, and an uninsured driving record can make you a higher-risk driver.
The Importance of Coverage
Even if your state doesn’t require car insurance, it’s crucial to have adequate coverage. Driving without insurance puts you at significant financial risk, potentially leading to substantial financial burdens in the event of an accident.
Insurance coverage acts as a safety net, protecting you from the potentially devastating costs associated with accidents. It helps cover expenses like medical bills, vehicle repairs, and legal fees, alleviating the financial strain that can arise from unforeseen events.
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
Understanding the different types of car insurance coverage is essential for making informed decisions about your insurance needs. Each type of coverage provides specific protection, and choosing the right combination can ensure you have adequate financial protection in the event of an accident.
- Liability Coverage: This coverage is the most common and is usually required by law. It protects you financially if you cause an accident that injures another person or damages their property. Liability coverage typically includes bodily injury liability and property damage liability.
- Collision Coverage: Collision coverage protects you if your vehicle is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. It covers the cost of repairs or replacement, minus your deductible.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This coverage protects you against damage to your vehicle from events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters. Like collision coverage, it covers the cost of repairs or replacement, minus your deductible.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This coverage protects you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who is uninsured or underinsured. It covers your medical expenses and property damage, up to the limits of your policy.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): PIP coverage, also known as no-fault insurance, covers your medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. This coverage is typically required in states with no-fault insurance laws.
- Medical Payments Coverage (Med Pay): Med Pay coverage pays for your medical expenses, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. It is a supplemental coverage that can be added to your policy.
Essential Car Insurance Coverage Options
| Coverage Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Liability Coverage | Protects you financially if you cause an accident that injures another person or damages their property. |
| Collision Coverage | Covers the cost of repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. |
| Comprehensive Coverage | Covers damage to your vehicle from events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters. |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage | Protects you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who is uninsured or underinsured. |
| Personal Injury Protection (PIP) | Covers your medical expenses and lost wages, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. |
| Medical Payments Coverage (Med Pay) | Pays for your medical expenses, regardless of who is at fault in an accident. |
Concluding Remarks: What States Don’t Need Car Insurance
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to purchase car insurance in a state that doesn’t mandate it is a personal one. While it might seem tempting to save money by forgoing coverage, the potential risks and consequences can be significant. It’s essential to weigh the potential financial, legal, and personal implications before making a decision. Understanding the complexities of car insurance in these states, including the financial responsibility laws and available alternatives, is crucial for making an informed choice that aligns with your individual needs and circumstances.
FAQ Insights
What happens if I get into an accident in a state that doesn’t require car insurance?
If you’re involved in an accident in a state without mandatory car insurance, you’ll be held financially responsible for any damages or injuries you cause. This could include medical bills, property repairs, and legal fees. Even if you’re not at fault, you could be held liable for the other driver’s losses.
Are there any benefits to driving without insurance in a state that doesn’t require it?
The primary benefit of driving without insurance is the potential to save money on monthly premiums. However, this savings comes with significant risks, as you’ll be fully responsible for any damages or injuries you cause in an accident.
What are some alternatives to traditional car insurance in states that don’t require it?
Some alternatives to traditional car insurance include self-insurance, surety bonds, and alternative insurance programs offered by some insurance companies. However, these options often have their own limitations and may not provide the same level of protection as traditional insurance.







