States that don’t require car insurance present a unique landscape for drivers, offering freedom from mandatory coverage but raising questions about financial responsibility and safety. While some states choose not to mandate car insurance, they still implement financial responsibility laws, requiring drivers to prove their ability to cover potential damages in case of accidents. This approach, while offering flexibility, can create challenges for accident victims seeking compensation from uninsured drivers.
The absence of mandatory insurance in certain states raises critical questions about the balance between individual freedom and collective safety. This article explores the legal implications, potential risks, and alternative methods of demonstrating financial responsibility in states without mandatory car insurance, providing insights into the complex interplay of personal choice and societal well-being on the road.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
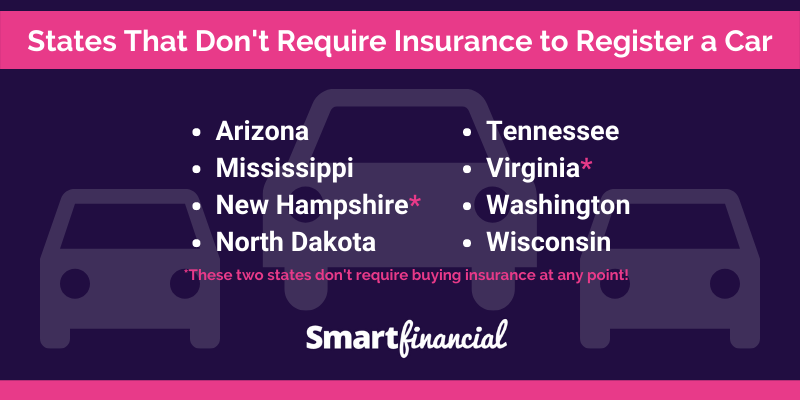
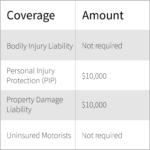
In the United States, all states require drivers to have some form of liability insurance, except for New Hampshire and Virginia. However, even in these states, drivers can face serious consequences if they are involved in an accident without insurance.
Legal Implications of Driving Without Insurance in States Without Mandatory Coverage
In New Hampshire and Virginia, drivers are not required to have car insurance, but they must be able to demonstrate financial responsibility in the event of an accident. This means that they must be able to pay for any damages or injuries they cause to others. Drivers in these states can meet this requirement by:
- Purchasing a surety bond, which guarantees payment for damages caused by the driver.
- Providing proof of sufficient assets, such as cash or property, to cover potential damages.
- Obtaining a self-insurance certificate, which certifies that the driver is financially responsible.
Potential Risks and Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without insurance in any state, even those that do not require it, can lead to significant risks and consequences, including:
- Financial Liability: In the event of an accident, drivers without insurance are personally responsible for all damages and injuries they cause. This can include medical bills, property damage, lost wages, and legal fees. Without insurance, drivers could face financial ruin if they are found liable for a serious accident.
- License Suspension: Even in states without mandatory insurance, driving without proof of financial responsibility can lead to license suspension. This can make it difficult to drive legally and can have a significant impact on daily life.
- Legal Penalties: Drivers who are caught driving without insurance can face fines, court costs, and even jail time. The specific penalties vary by state.
- Difficulty Obtaining Insurance: If a driver has a history of driving without insurance, they may find it difficult to obtain insurance in the future. Insurance companies may view them as a high-risk driver and charge higher premiums or refuse to cover them altogether.
Financial Liability in Case of Accidents
In states without mandatory insurance, drivers who are involved in an accident are fully responsible for the damages they cause. This means that they could be held liable for:
- Medical Expenses: If the driver causes injuries to others, they will be responsible for all medical bills, including hospital stays, surgeries, rehabilitation, and ongoing care.
- Property Damage: If the driver damages another person’s vehicle or property, they will be responsible for the cost of repairs or replacement.
- Lost Wages: If the driver causes injuries that prevent others from working, they could be held liable for lost wages.
- Pain and Suffering: In some cases, the driver may also be held liable for pain and suffering, which can include emotional distress, physical pain, and loss of enjoyment of life.
It is important to note that even if a driver is not required to have car insurance, they are still legally obligated to provide proof of financial responsibility in the event of an accident. This means that they must be able to pay for any damages or injuries they cause to others.
Financial Responsibility Laws
Even though some states don’t require car insurance, they all have financial responsibility laws in place to ensure that drivers can cover the costs of accidents they cause. These laws protect victims and ensure that drivers are held accountable for their actions on the road.
Financial responsibility laws are designed to make sure that drivers have the means to pay for damages or injuries caused by an accident. These laws often require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility, such as insurance, surety bonds, or cash deposits, to demonstrate their ability to cover potential liabilities.
Types of Financial Responsibility Laws
States without mandatory car insurance typically have one of three main types of financial responsibility laws:
- Financial Responsibility Law: This type of law requires drivers to demonstrate proof of financial responsibility only after they have been involved in an accident. This means that they are not required to carry insurance beforehand but must provide proof of financial responsibility to cover the costs of the accident.
- Security Responsibility Law: These laws are more proactive and require drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility before they can register their vehicle. This typically involves providing evidence of insurance or other forms of financial responsibility, such as a surety bond.
- Compulsory Financial Responsibility Law: This type of law requires drivers to maintain a minimum amount of financial responsibility at all times, similar to mandatory car insurance laws. Drivers must provide proof of insurance or other forms of financial responsibility to the state.
Impact of Financial Responsibility Laws on Drivers
Financial responsibility laws can have a significant impact on drivers, especially in states without mandatory car insurance. Here are some examples of how these laws affect drivers in practice:
- After an Accident: If a driver is involved in an accident and does not have proof of financial responsibility, they may face severe consequences. This could include fines, license suspension, or even the impounding of their vehicle. The driver may also be held personally liable for all damages and injuries caused by the accident, potentially leading to financial ruin.
- Registration and Driving Privileges: Drivers may be required to provide proof of financial responsibility before they can register their vehicle or obtain a driver’s license. This ensures that all drivers on the road have some level of financial responsibility.
- Potential Financial Burden: Even with financial responsibility laws, drivers may still face significant financial burdens if they are involved in an accident. They may have to pay for repairs, medical bills, or other expenses out of pocket.
Alternatives to Traditional Car Insurance

In states that don’t require car insurance, drivers have alternative options to demonstrate financial responsibility. These alternatives can offer advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional car insurance.
Surety Bonds
Surety bonds are financial instruments that guarantee the payment of a specific sum of money in case of an accident. The bond issuer, typically an insurance company, guarantees the payment of damages up to the bond amount. The driver pays a premium to the bond issuer, and the bond is filed with the state’s Department of Motor Vehicles.
- Pros: Surety bonds can be less expensive than traditional car insurance, especially for drivers with good driving records. They can also offer more flexibility in coverage options.
- Cons: Surety bonds may not cover all potential losses, and they may be difficult to obtain if the driver has a poor credit history or a history of accidents.
Obtaining a surety bond typically involves providing the bond issuer with personal information, driving history, and financial information. The bond issuer will then assess the risk and determine the premium and the bond amount. Maintaining a surety bond requires paying the premiums on time and keeping the bond issuer informed of any changes in personal or financial information.
Self-Insurance
Self-insurance is a method of financial responsibility where the driver sets aside a specific amount of money to cover potential losses in case of an accident. This money is typically kept in a savings account or a dedicated investment account.
- Pros: Self-insurance can be a cost-effective option for drivers who have a good driving record and are confident in their ability to manage their finances.
- Cons: Self-insurance requires a significant amount of financial discipline and planning. It also carries the risk of financial hardship if a major accident occurs and the driver’s savings are insufficient to cover the losses.
Self-insurance requires careful planning and budgeting. Drivers need to determine the amount of money they need to set aside, based on factors such as their driving history, the value of their vehicle, and their estimated annual driving mileage. They should also consider the potential costs of repairs, medical expenses, and legal fees. Maintaining self-insurance involves regularly contributing to the dedicated fund and monitoring the balance to ensure it is sufficient to cover potential losses.
Impact on Drivers and Accidents
Driving without insurance can have significant consequences for both drivers and accident victims. The lack of financial protection can lead to severe financial hardship and legal complications.
Consequences for Uninsured Drivers
Drivers without insurance face numerous challenges in the event of an accident. They may be held personally liable for all damages and injuries, potentially leading to:
- Financial Ruin: Uninsured drivers are responsible for covering all costs associated with the accident, including medical expenses, property damage, legal fees, and potential court judgments. These expenses can quickly drain their savings and assets.
- Legal Battles: Accident victims can sue uninsured drivers to recover compensation for their losses. Uninsured drivers may face lawsuits, judgments, and even wage garnishment to satisfy the claims.
- License Suspension or Revocation: In many states, driving without insurance is illegal and can result in license suspension or revocation. This can severely restrict their ability to drive and negatively impact their livelihood.
- Criminal Charges: Some states consider driving without insurance a criminal offense, leading to fines, jail time, or both.
Challenges for Accident Victims
Accident victims who are involved with an uninsured driver face significant hurdles in obtaining compensation. Uninsured drivers may be unable or unwilling to pay for the damages they caused, leaving victims with substantial financial burdens.
- Difficulty in Recovery: Victims may have to file lawsuits against the uninsured driver to recover compensation, but the process can be lengthy and expensive. It is difficult to collect from an uninsured driver who may have limited assets or be unwilling to pay.
- Uninsured Motorist Coverage: Accident victims may be able to recover some compensation through their own insurance policy’s uninsured motorist coverage (UM). However, UM coverage often has limits, and the payout may not fully cover the victim’s losses.
- Financial Hardship: Victims may face significant financial hardship due to medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage. Without insurance, they may have to shoulder these costs themselves, leading to debt and financial instability.
Real-World Examples
- Scenario 1: A driver without insurance causes a serious accident, injuring the other driver and damaging their vehicle. The uninsured driver is held liable for the damages, but they have no insurance to cover the costs. The injured driver faces significant medical bills and lost wages, and the property damage may not be fully covered.
- Scenario 2: A pedestrian is struck by an uninsured driver. The pedestrian suffers serious injuries and requires extensive medical treatment. The uninsured driver cannot afford to pay for the medical expenses, leaving the victim with substantial debt and a long recovery process.
Safety Considerations
Driving without insurance can have significant safety implications, raising concerns about the potential lack of financial incentives to drive responsibly. This section delves into the potential safety implications of driving without insurance, explores the correlation between insurance coverage and driving behavior, and compares the safety statistics of states with and without mandatory car insurance.
Impact of Insurance on Driving Behavior
The presence of car insurance can influence driving behavior in several ways. Insurance provides financial protection in case of accidents, potentially encouraging drivers to be more cautious. The fear of financial repercussions for accidents, such as increased premiums or policy cancellation, can act as a deterrent to reckless driving.
“Drivers with insurance are more likely to be financially responsible for their actions, potentially leading to safer driving habits.”
Safety Statistics Comparison
A comparison of safety statistics between states with and without mandatory car insurance can provide insights into the potential impact of insurance on road safety. The following table presents a simplified comparison:
| Feature | States with Mandatory Car Insurance | States Without Mandatory Car Insurance |
|—|—|—|
| Number of Uninsured Drivers | Lower | Higher |
| Average Number of Accidents per Year | Lower | Higher |
| Average Severity of Accidents | Lower | Higher |
| Fatality Rate | Lower | Higher |
Note: This is a simplified representation, and other factors can influence safety statistics. However, the data generally suggests a correlation between mandatory car insurance and improved road safety.
Future Trends and Considerations: States That Don’t Require Car Insurance
The landscape of car insurance in states without mandatory coverage is dynamic and subject to various influences, including technological advancements, societal shifts, and evolving legal interpretations. Understanding these trends is crucial for policymakers, insurance providers, and drivers alike.
Potential Future Trends in States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
Several factors could shape the future of car insurance in these states.
- Increased Use of Telematics: Telematics devices and applications that monitor driving behavior are becoming increasingly prevalent. This data can be used to personalize insurance premiums based on individual driving habits, potentially incentivizing safer driving practices.
- Growth of Usage-Based Insurance (UBI): UBI programs offer flexible coverage options that adjust premiums based on actual driving patterns, such as mileage, time of day, and braking behavior. This approach could become more popular in states without mandatory coverage, as it provides greater control and potential savings for drivers.
- Expansion of Alternative Insurance Models: Innovative insurance models like peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance, where drivers pool their risks and share costs, could gain traction in states without mandatory coverage. These models often rely on technology and community engagement, offering flexibility and potentially lower premiums.
- Greater Emphasis on Financial Responsibility: States without mandatory car insurance may adopt stricter financial responsibility laws, requiring drivers to demonstrate their ability to cover potential damages in case of an accident. This could involve higher minimum liability limits or increased enforcement of existing laws.
- Increased Awareness and Education: Efforts to educate drivers about the risks and financial consequences of driving without insurance may lead to a greater understanding of the importance of coverage. This could potentially result in more drivers voluntarily choosing to purchase car insurance.
Arguments for and Against Implementing Mandatory Car Insurance, States that don’t require car insurance
The debate over mandatory car insurance in states without such requirements is complex and multifaceted.
- Arguments for Mandatory Car Insurance:
- Enhanced Road Safety: Mandatory insurance encourages drivers to be financially responsible, reducing the likelihood of uninsured drivers fleeing the scene after accidents or avoiding liability. This could contribute to a safer driving environment.
- Protection for Uninsured Victims: Uninsured drivers pose a significant risk to other road users. Mandatory insurance ensures that victims of accidents involving uninsured drivers have access to compensation for medical expenses, property damage, and lost wages.
- Reduced Costs for Society: The burden of uninsured motorist accidents often falls on taxpayers and insurers through programs like the uninsured motorist fund. Mandatory insurance can help mitigate these costs by spreading the risk more equitably.
- Arguments Against Mandatory Car Insurance:
- Increased Costs for Drivers: Mandatory insurance could lead to higher premiums for all drivers, even those with good driving records. This could disproportionately impact low-income individuals and families.
- Government Overreach: Some argue that mandatory insurance represents government overreach into personal financial decisions. They believe individuals should have the freedom to choose whether or not to purchase insurance.
- Potential for Unintended Consequences: Implementation of mandatory insurance could lead to unintended consequences, such as increased administrative costs, insurance fraud, or a decline in the availability of affordable insurance options.
Potential Timeline of Policy Changes
It is difficult to predict a specific timeline for policy changes related to car insurance in states without mandatory coverage. However, several factors could influence the pace and direction of such changes.
- Increased Public Awareness: As the public becomes more aware of the risks associated with driving without insurance, there may be growing pressure on policymakers to consider mandatory coverage.
- Legislative Initiatives: Bills proposing mandatory car insurance could be introduced in state legislatures, potentially leading to debates and eventual policy changes.
- Judicial Decisions: Court rulings related to uninsured motorist accidents or financial responsibility laws could influence the legal landscape and shape future policy decisions.
- Industry Trends: Insurance industry trends, such as the adoption of new technologies or the emergence of alternative insurance models, could influence the way car insurance is regulated and provided.
End of Discussion
Navigating the world of driving without mandatory car insurance requires careful consideration of financial responsibility, safety implications, and potential consequences. While states without mandatory insurance offer flexibility, drivers must actively explore alternative methods of demonstrating financial responsibility to protect themselves and others. Ultimately, understanding the legal framework, potential risks, and available options empowers drivers to make informed decisions that balance personal freedom with responsible driving practices.
Answers to Common Questions
What happens if I get into an accident in a state that doesn’t require car insurance?
If you’re involved in an accident in a state without mandatory car insurance, you could face significant financial liability for damages, injuries, and medical expenses. Even if you are not at fault, you may be held responsible for the other driver’s losses if they are uninsured.
How can I prove financial responsibility in a state without mandatory car insurance?
States without mandatory car insurance often require drivers to demonstrate financial responsibility through alternative methods like surety bonds, self-insurance, or proof of sufficient assets. These methods ensure that you can cover potential costs associated with accidents.
Are there any penalties for driving without insurance in states that don’t require it?
While states without mandatory car insurance don’t require it, they often have financial responsibility laws that can result in fines, license suspension, or even jail time if you’re found driving without sufficient financial coverage.
Is it cheaper to drive without insurance in states that don’t require it?
It’s important to remember that driving without insurance is a significant risk. While you may save on premiums, the potential financial consequences of an accident can far outweigh any perceived savings.