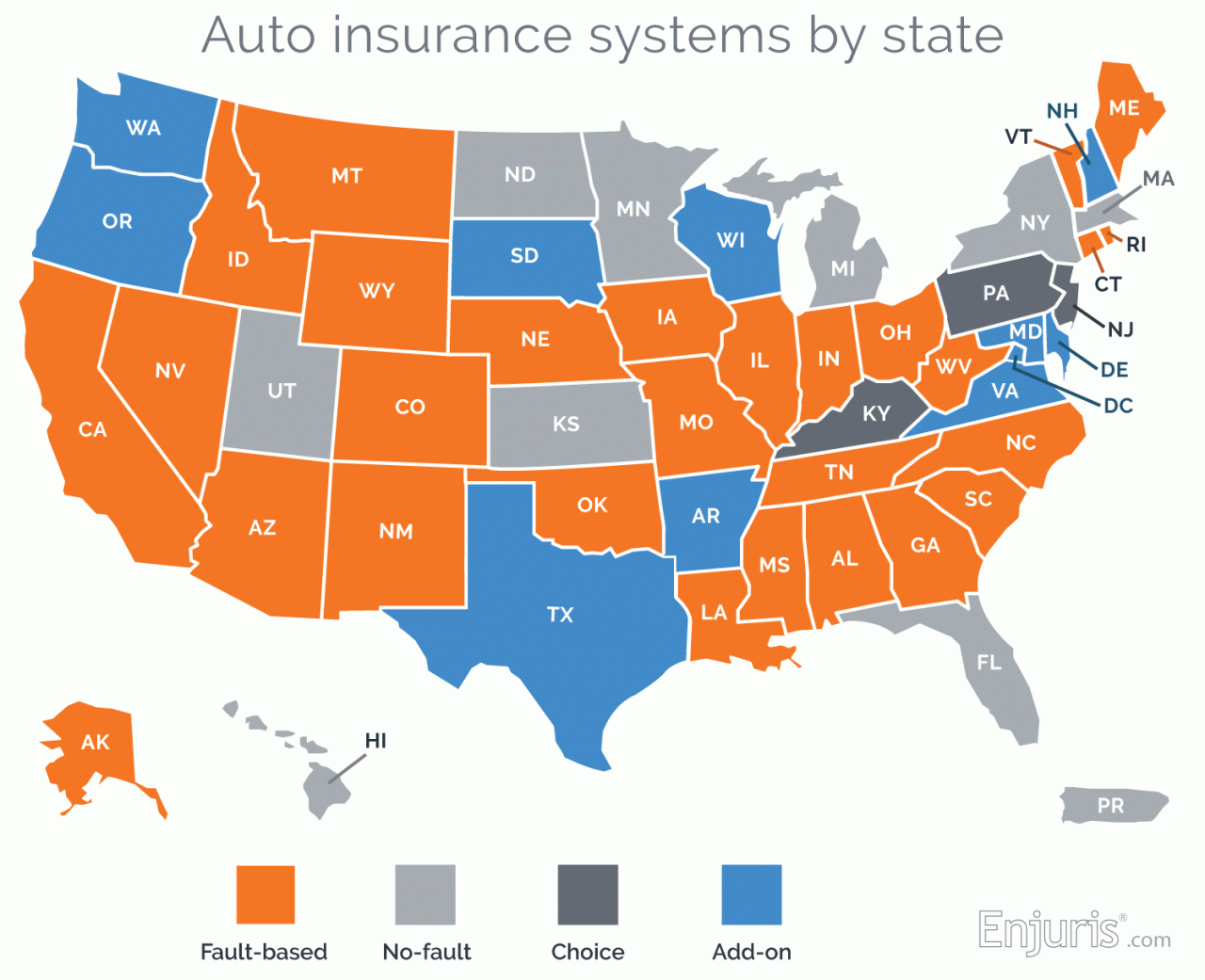
What states don’t require car insurance? This question often sparks curiosity and concern among drivers. While most states mandate car insurance, a few exceptions exist. Understanding these exceptions is crucial for drivers, as it directly impacts their financial responsibility and potential legal consequences. In this article, we’ll explore the states that don’t require car insurance, delve into the legal implications of driving without it, and examine the financial risks involved.
This article will shed light on the complexities of financial responsibility laws and their varying interpretations across states. We’ll uncover specific exemptions and exceptions to mandatory car insurance requirements, providing insights into situations where individuals may be exempt from this obligation. Additionally, we’ll examine the potential consequences of driving without insurance, including fines, license suspension, and legal repercussions. We’ll also explore alternative options to traditional car insurance for those seeking coverage in states without mandatory requirements.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
While most states in the U.S. require drivers to carry car insurance, a few states do not have a mandatory car insurance law. These states often have different regulations and consequences for driving without insurance.
States Without Mandatory Car Insurance
These states do not have a mandatory car insurance requirement, meaning drivers are not legally obligated to purchase car insurance:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
However, it is important to note that even in these states, there are specific circumstances where car insurance is still required. For instance, drivers who have a car loan or lease are usually required to have car insurance by the lender.
Legal Implications of Driving Without Insurance in These States
Although these states do not mandate car insurance, driving without insurance can still have significant legal implications. In New Hampshire, for example, drivers without insurance face potential financial consequences if they are involved in an accident. While Virginia allows drivers to choose whether or not to purchase car insurance, the state offers a program called the Virginia Uninsured Motorist Fund (UMF) that can provide compensation to accident victims who are injured by uninsured drivers.
Financial Consequences for Drivers Without Insurance
Even in states without mandatory car insurance, drivers who choose not to have insurance face a significant risk. In the event of an accident, they could be held financially responsible for:
- Damage to other vehicles: Drivers without insurance may be liable for the entire cost of repairs to the other vehicle involved in the accident.
- Medical expenses: If the accident results in injuries, the uninsured driver may be responsible for covering the medical bills of the injured party.
- Legal fees: In the event of a lawsuit, uninsured drivers could face substantial legal fees.
- Loss of driving privileges: Depending on the state and the severity of the accident, driving without insurance could lead to the suspension or revocation of driving privileges.
In addition to these financial consequences, driving without insurance can also have a significant impact on a driver’s credit score, making it more difficult to obtain loans or credit cards in the future.
Financial Responsibility Laws

Financial responsibility laws are designed to ensure that drivers have the financial means to cover the costs of any accidents they cause. These laws are crucial for protecting other drivers, passengers, and pedestrians in the event of an accident.
While all states have some form of financial responsibility law, the specific requirements and penalties vary widely.
Financial Responsibility Laws in Different States
Financial responsibility laws differ significantly from state to state, impacting drivers in various ways. Here are some examples:
- Some states require drivers to carry a minimum amount of liability insurance, while others allow drivers to provide proof of financial responsibility through a surety bond or self-insurance.
- The minimum liability insurance requirements vary widely between states, ranging from $10,000 to $50,000 or more per accident.
- Some states have “no-fault” insurance systems, where drivers are primarily responsible for covering their own losses, regardless of who caused the accident.
- Other states have “tort” systems, where drivers can sue the at-fault party for damages.
Penalties for Violating Financial Responsibility Laws
The penalties for violating financial responsibility laws can be severe and vary depending on the state and the specific violation. Here are some common penalties:
- Fines: Drivers who fail to meet the financial responsibility requirements can face fines ranging from a few hundred dollars to thousands of dollars.
- License Suspension: States may suspend the driver’s license of those who fail to comply with financial responsibility laws.
- Vehicle Impoundment: The vehicle of a driver who violates financial responsibility laws may be impounded until the driver provides proof of insurance.
- Jail Time: In some cases, drivers who repeatedly violate financial responsibility laws may face jail time.
Exceptions and Exemptions
While most states require car insurance, some exceptions and exemptions exist. These exceptions are usually granted to specific groups or situations. For example, some states may exempt vehicles used for specific purposes, such as those used for farming or commercial transportation. Other exemptions may apply to individuals who are financially unable to afford car insurance.
Exemptions for Specific Vehicles
Certain vehicles may be exempt from mandatory car insurance requirements. These exemptions typically apply to vehicles that are not used for regular transportation, such as:
- Vehicles used for agricultural purposes
- Vehicles used for commercial transportation
- Vehicles used for military purposes
- Vehicles used for government purposes
- Vehicles used for recreational purposes, such as motorcycles or off-road vehicles
The specific requirements for each exemption may vary from state to state. For instance, some states may require that vehicles used for agricultural purposes be registered and insured as farm vehicles, while others may exempt them altogether. It’s important to consult your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles for specific information regarding vehicle exemptions.
Exemptions for Individuals
Certain individuals may be exempt from car insurance requirements based on their financial situation or other circumstances. For instance, some states may exempt individuals who:
- Are unable to afford car insurance due to financial hardship
- Are covered by a different type of insurance, such as a business policy
- Are considered high-risk drivers and cannot obtain insurance from private insurers
- Are uninsured because they have a valid reason, such as a recent accident or a driving violation
These exemptions are usually granted on a case-by-case basis and require documentation to prove the individual’s eligibility. The criteria for qualifying for these exemptions can vary significantly from state to state, so it’s crucial to consult with your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles or an insurance professional for accurate information.
Consequences of Driving Without Insurance
Driving without car insurance is not only against the law in most states but also carries significant financial and legal risks. Even in states that do not mandate car insurance, it is highly advisable to have it, as it provides financial protection in case of an accident.
Fines and License Suspension
Driving without insurance is a serious offense in most states, and drivers caught doing so can face severe penalties.
- Fines: Drivers can be fined hundreds or even thousands of dollars, depending on the state and the number of offenses. These fines can vary significantly, with some states imposing fines of up to $1,000 for a first offense.
- License Suspension: In addition to fines, drivers may have their licenses suspended or revoked. This can make it impossible to drive legally, further impacting their ability to commute, work, and carry out daily tasks.
Legal Repercussions
Driving without insurance can have significant legal repercussions, especially in the event of an accident.
- Liability: If you cause an accident without insurance, you could be held personally liable for all damages, including medical bills, property damage, and lost wages. This could result in substantial financial losses and even bankruptcy.
- Lawsuits: The injured party may file a lawsuit against you, seeking compensation for their injuries and losses. Without insurance, you will have to bear the full cost of defending yourself in court and potentially pay significant damages.
Financial Burden
Accidents without insurance coverage can lead to a significant financial burden.
- Medical Expenses: Even a minor accident can result in substantial medical bills. Without insurance, you will be responsible for all medical expenses, including emergency room visits, surgeries, and long-term care.
- Property Damage: Accidents can cause significant damage to vehicles and property. Without insurance, you will be responsible for repairing or replacing damaged vehicles and property, which can be extremely expensive.
- Lost Wages: If you are injured in an accident, you may be unable to work, resulting in lost wages. Without insurance, you will have to cover these lost wages out of pocket.
Real-World Examples
There have been numerous cases where drivers without insurance faced severe consequences.
- In a 2023 case in California, a driver without insurance caused a serious accident, injuring three people. The driver was found liable for the accident and was ordered to pay over $1 million in damages. The driver was also sentenced to six months in jail.
- In a 2022 case in Florida, a driver without insurance hit a pedestrian, causing severe injuries. The driver was found guilty of reckless driving and was sentenced to five years in prison. The driver was also ordered to pay over $500,000 in damages to the pedestrian.
Alternatives to Traditional Car Insurance: What States Don’t Require Car Insurance
In states that don’t mandate car insurance, drivers have the option to explore alternatives to traditional coverage. These alternatives provide financial protection in case of accidents, but they differ in their coverage, costs, and suitability for different drivers.
Self-Insurance, What states don’t require car insurance
Self-insurance is a way to cover potential losses from accidents by setting aside a specific amount of money in a dedicated account. This approach allows drivers to manage their risk and potentially save on insurance premiums.
- Pros:
- Potential for cost savings: Drivers who are risk-tolerant and have a good driving record may save money by self-insuring.
- Flexibility: Self-insurance offers flexibility in managing coverage and choosing how to allocate funds.
- Cons:
- High financial risk: Self-insurance requires drivers to cover all accident costs, which can be substantial.
- Limited coverage: Self-insurance may not cover all potential losses, such as injuries to others or property damage.
- Potential for financial hardship: A significant accident could lead to financial hardship for self-insured drivers.
Surety Bonds
A surety bond is a financial guarantee issued by a surety company that protects the bondholder against financial losses caused by the bonded party. In the context of car insurance, a surety bond can provide financial protection for accidents, similar to traditional insurance.
- Pros:
- Financial protection: A surety bond can provide financial protection for accidents, ensuring that the bondholder is covered for losses.
- Potential for cost savings: Surety bonds may be more affordable than traditional insurance, especially for drivers with good driving records.
- Cons:
- Limited coverage: Surety bonds may not cover all potential losses, such as injuries to others or property damage.
- Potential for higher costs: In some cases, surety bonds can be more expensive than traditional insurance, especially for drivers with poor driving records.
- Limited availability: Surety bonds may not be available in all states or for all types of vehicles.
Other Alternatives
Besides self-insurance and surety bonds, other alternatives to traditional car insurance exist. These options may be more suitable for certain drivers, depending on their needs and circumstances.
- Cash-based insurance: This option allows drivers to pay for accident costs out of pocket, avoiding insurance premiums altogether. However, it requires significant financial reserves to cover potential losses.
- Ride-sharing or carpooling: Drivers can reduce their reliance on car ownership by using ride-sharing services or carpooling, which can significantly reduce the need for car insurance.
- Membership-based insurance: Some organizations offer membership-based insurance programs that provide limited coverage for accidents. These programs may be more affordable than traditional insurance, but they often have lower coverage limits.
Conclusive Thoughts
Ultimately, driving without car insurance in states that don’t require it comes with significant risks. While it may seem tempting to forgo insurance, the potential financial and legal repercussions are substantial. It’s crucial to understand the specific laws in your state and to take necessary precautions to protect yourself and others on the road. By navigating the complexities of financial responsibility laws and exploring alternative options, drivers can make informed decisions about their insurance needs and minimize their risk exposure.
Helpful Answers
What are the consequences of driving without insurance in a state that requires it?
The consequences vary depending on the state, but they can include fines, license suspension, and even jail time. You may also be required to pay for any damages you cause in an accident.
What are the benefits of having car insurance, even in states that don’t require it?
Even if you’re not legally required to have car insurance, it’s still a good idea to have it. Car insurance protects you financially in case of an accident, and it can also help you avoid hefty fines and other penalties.
What are some of the most common exemptions from car insurance requirements?
Some common exemptions include vehicles used for agricultural purposes, antique cars, and vehicles that are only driven on private property. However, it’s important to check the specific requirements in your state.